click to enlarge

Green Box with 94 Items
© 1999 Succession Marcel Duchamp, ARS,
N.Y./ADAGP, Paris.
click to enlarge

Museum of Modern Art Lab.
In 1934, Marcel Duchamp announced the publication of his Green Box (edition of 320 copies) in a subscription bulletin — an enormous undertaking since each box contains 94 individual items mostly supposed “facsimiles” (Duchamp’s word) of notes first written between 1911 and 1915, each printed and torn upon templates to match the borders of the scribbled originals for a total of 30,080 scraps and pages.(1)
(See illustrations 1A & 1B for The Bride Stripped Bare by her Bachelors, Even in deluxe and regular editions; illustration 1C for the Subscription Bulletin advertising the Green Box in 1934; and illustration 1D for Duchamp’s master work a.k.a. The Large Glass (1915-23) of the same title as the Green Box.) Spectators, according to Duchamp, needed to study this “Sears Roebuck-like catalogue” of notes in order to understand his major life’s work, The Large Glass (also known by the same title as the Green Box: The Bride Stripped Bare by her Bachelors, Even).
Calvin Tomkins, Duchamp’s biographer, in 1996 writes:
Duchamp had always maintained that his Glass was not just something to be looked at but “an accumulation of ideas,” in which verbal elements were at least as important as visual ones, perhaps even more so. […] As Duchamp would say in a 1959 interview, he had “tried in that big Glass to find a completely personal and new means of expression; the final product was to be a wedding of mental and visual reactions; in other words, the ideas in the Glass were more important than the actual visual realization.” Since the ideas were contained (more or less) in
the notes, their long-delayed publication would become a new chapter in the continuing saga of his unfinished, shattered, but far from defunct masterpiece.(2)
Duchamp famously boasted — and the claim has been repeated, mantra-like, in nearly all commentary and scholarship upon Duchamp — that he had exerted enormous, almost maniacal, effort to reproduce the notes exactly, down to details of paper and ink.(3)He told Michel Sanouillet in 1954, for example:
I wanted to reproduce them as accurately as possible. So I had all of these thoughts lithographed in the same ink which had been used for the originals. To find paper that was exactly the same, I had to ransack the most unlikely nooks and crannies of Paris.Then we cut out three hundred copies of each lithograph with the help of zinc patterns that I had cut out on the outlines of the original papers.(4)
Scholars have accepted Duchamp’s claims at face value, uncritically adopting Duchamp’s given words as a premise in their own “analysis.” For example, Calvin Tomkins refers to Duchamp’s “absolute fidelity to the physical appearance” of his Green Box Notes as “puzzling” since they were based upon abstract ideas.(5) Elizabeth Cowling writes in 1997; “Duchamp adopted the most time consuming and meticulous methods,scouring the specialist suppliers in Paris for papers that were exactly like those on which he had originally made his notes, and for lithographic inks of exactly the same color as the inks,etc. he had used.”(6) And David Joselit writes in 1998: “Duchamp took extraordinary pains to mass-produce what is generally assumed to be unique or original — the artist’s cognitive process. It was not enough to publish transcripts of his texts. Rather he sought to reproduce as precisely as possible each torn piece of paper, each different ink, so that every one of the proposed three hundred editions of the Green Box would appear to share the spontaneity, the immediacy of the original process — as though he had undertaken to mass-produce his own subjectivity discovered readymade.”(7)
Let us leave aside for now (and for later and more extensive commentary) the deliciously ironic issue of why conventional scholarship on a man so celebrated for tweaking and mocking conventionality should be so willing to accept the subject’s own statements about his intentions and procedures as a kind of holy writ — and not suspect that Duchamp might also have played games by preying upon their gullibility and hagiographical tendencies as well. In any case, we merely wish to point out here that Duchamp, manifestly and purposefully, did not proceed as advertised in compiling the Green Box — and that scholars have not thought to check his claims, even though the material for so doing (comparison of the original and reproduced notes) has always been available.
click to enlarge

Illustration 2A
© 1999 Succession Marcel
Duchamp, ARS,N.Y./ADAGP, Paris

Illustration 2B
© 1999 Succession Marcel
Duchamp, ARS, N.Y./ADAGP, Paris
click to enlarge

Illustration 3A
© 1999 Succession Marcel
Duchamp, ARS, N.Y./ADAGP, Paris .
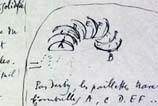
Illustration 3B
© 1999 Succession Marcel
Duchamp, ARS, N.Y./ADAGP, Paris.
Most of the original notes remained with Duchamp and were not accessible to scholars during his life. But they then passed to his estate, and thence to the Centre Georges Pompidou (Paris), where they are now freely available for scholarly study. Moreover, and more importantly,a substantial group of these notes have always been potentially available to researchers — and comparisons between the originals and the Green Box so-called facsimiles could always have been made, although none ever were. Duchamp produced a special edition of 20 deluxe boxes (out of the total edition of 320), each containing one original note, along with 93 reproductions.
Several owners of the 20 Deluxe Green Boxes sold the original notes (contained within them) separately, and Shearer was able to procure one of the original notes.(8)Shearer’s note discusses a long, complex and important statement about the malic molds and sieves in the bachelor half of The Large Glass. (See illustrations 2A & 2B, Shearer’s original note and the Green Box reproduction.) She noticed immediately that neither the ink nor the paper of the original note matched the reproductions in two copies of the Green Box. The original is written in black ink, but the Green Box versions use blue ink in the lithographic reproduction. (see illustrations 3A & 3B which compare the original note’s textured paper and the reproduction’s paper) The original paper is thin, textured and warm in tone. The Green Box reproduction’s paper is much thicker, bluish in tone and smooth.If Duchamp “wanted to reproduce [the notes] as exactly as possible,” why would he replicate other Green Box notes with paper similar in texture to Shearer’s original note, but then not use this same paper in reproducing Shearer’s note? (See illustration 3C showing example of Green Box note with texture.)
click to enlarge

Illustration 3C
© 1999 Succession Marcel
Duchamp, ARS, N.Y./ADAGP, Paris.
Shearer and Gould then consulted Margaret Holben Ellis at the New York University Institute of Fine Arts, and Christopher McGlinchey and Erika Mosier at the Museum of Modern Art Conservation to learn if the difference in ink color could have resulted from a natural change through time from Duchamp’s original. Christopher McGlinchey, from his chemical analysis, identified the ink in the original note as lamp black and in the reproduction as Prussian blue. McGilnchey assures us that the lampblack ink in the original note was not ever blue (as used in the reproduction), and that the inks are truly different.(9) See illustrations 3A & 3B showing detail of Prussian blue ink in the Green Box copy and lamp black ink in the original note.) Moreover, the wove paper used by Duchamp in the Green Box could not represent the closest likeness available after scouring all the stores of Paris, because machine-laid paper much more similar (if not identical) to Duchamp’s original can still be easily obtained and was surely available when Duchamp made the Green Box.(10)(After all, he used machine-laid paper in other Green Box note reproductions.)Clearly, Duchamp intentionally altered both ink and paper to depart from the originals in his “facsimile” copies despite his claims, beginning in 1934, for faithful reproduction.
click to enlarge

Illustration 5A
© 1999 Succession Marcel Duchamp,
ARS, N.Y./ADAGP, Paris

Illustration 5B
© 1999 Succession Marcel
Duchamp, ARS, N.Y./ADAGP, Paris.
We then checked further to discover whether these alterations are systematic throughout the Green Box, or merely incidental in a few notes. Shearer and Gould examined 22 original notes at the Pompidou Center and we now wish to present this preliminary report.We feel confident in stating, at this early stage of our investigation,that the differences are pervasive and systematic. Every one of the 22 notes we examined shows substantial difference between the original and the Green Box “copies.” On every note, Duchamp uses complex combinations of different papers and different inks in making the Green Boxversions.(11)Moreover, lest one think that Duchamp may simply have done the best he could with materials available, and that the differences represent “sins of omission” rather than “sins of commission” we can report conclusively that at least some of the changes were done with clear intent – for Duchamp’s own instructions remain in the original notes to prove the point. On the back of several one-sided notes, he wrote an instruction for the printer: tel recto seul – that is, “same size, right side only.” But two notes of the 22 we examined bear the “smoking gun” inscription: Ag 1/4 recto seul — that is, “enlarge by 1.25, right side only.” (See illustrations 5A & 5B, two of the notes which Duchamp selected to enlarge in reproductions.) The Green Box versions of these two notes are, indeed, 1.25 times larger than the originals.
Among further typical alterations in the 22 notes we find: the original note “laws, principles, phenomena” is written in blue ink but the Green Box version is printed in black ink, a reverse combination when compared to Duchamp’s alterations of Shearer’s original note — in black ink but “duplicated” in blue ink. In another case, he reproduced the “1912” note on graph paper with a square pattern whereas the original was on graph paper with a rectangular pattern. However, in the “chute d’éau” note, the original is not on graph paper, yet the Green Box version is printed on square patterned graph paper.(12)
click to enlarge

Illustration 6A
© 1999 Succession
Marcel Duchamp, ARS,
N.Y./ADAGP, Pari

Illustration 6B
© 1999 Succession
Marcel Duchamp, ARS,
N.Y./ADAGP, Paris
We strongly suspect that the differences between originals and Green Box versions are systematic rather than capricious — they are surely pervasive in any case — and we shall be studying all the available notes in an attempt to understand the system. But, for now and in closing, we wish to report one other remarkable fact.(13)
Duchamp’s wry and false claims that he worked so hard in scouring Paris for the right inks and papers covers up an enormously greater (and genuine) expenditure of time that he completely failed to stress!We first learned about this remarkable feature of Duchamp’s production when Margaret Ellis noted a pin prick through a period in both Green Box versions that we used for this study– but no pinprick in the original.(See illustrations 6A & 6B, showing original note without pin prick and reproduction with pin prick.) This led us to suspect that the pinprick probably anchored a stencil that Duchamp had used to produce part of the Green Box version.
click to enlarge

Illustration 6C
© 1999 Succession Marcel Duchamp, ARS,
N.Y./ADAGP, Paris.
Indeed, our study of several notes reveals that, although Duchamp always reproduced the background text by lithography when he added the words and phrases in red or blue highlight (often as they appear on the originals) he used pochoir stencils (a method he openly discussed and employed for promoting both his Boîte en Valise1934-41)and his< Eau et Gaz Box (1958)even featuring his inclusion of the actual pochoir stencils in his grand deluxe versions). (See illustration 6C for Duchamp’s Boîte; see illustration 7A for Duchamp posing with Lebel holding “pochoir stencils” sold with the grand deluxe Eau et Gaz and illustration 7B for pochoir stencil included in the grand deluxe version of Eau et Gaz.) Moreover, and more remarkably, he used two or more stencils for one color on some of the notes (to secure overlayerings as occurs in handwriting), even though the entire text of one color could have been reproduced with a single stencil. (See llustrations 8A & 8B comparing his use of two stencils for red showing overlap — similar to the results of handwriting — versus his use of one stencil for red.See also illustrations 8C & 8D which show the irregular texture of collotype lithography in one of Duchamp’s Green Box notes versus the smooth surface from a stencil that often shows varied pooling along edges upon close inspection.) (14)
Just consider the immense amount of work required to reproduce 320 copies of most of the 94 items in varied combinations of inks and papers that depart from the originals, often one at a time using multiple stencils. For example, Ellis and Mosier have assured us that Duchamp, as a printer with two years of professional training, would have known that he could have achieved far greater exactness in reproduction, and saved a great deal of money and even more time in what can only be regarded as meticulous and uninspiring work, by reproducing the red and blue highlights lithographically. Did he use this laborious method of stenciling to introduce inevitable and slight differences among the 320 boxes — differences that a careful observer could use to spot his methods, and to discover the inconsistencies between his actions and his explanations? Or does the hand stenciling create enough small, perceivable differences between each copy (and its original document) to force us to ask whether we encounter here a new category and strategy of reproduction — not a true “facsimile” (“to make similar”) but now a “facvarious” (“to make different”). This man never ceases to surprise us — and to instruct us about our foibles and assumptions.
The “original plates […] used in printing the manuscript notes for
click to enlarge

Illustration 9
© 1999 Succession
Marcel Duchamp, ARS,
N.Y./ADAGP, Paris.the Green Box” (as depicted in entry no. 436 in The Arturo Schwarz Duchamp Catalogue Raisonné [1998])are not printing plates according to Ellis and Mosier. We checked to see if these plates could have been the templates used by Duchamp to tear the edges of each reproduction in order to mimic the tears of the originals. Of the 23 plates only a few have the complete shape of the original note — the others would not work as successful templates for tearing the reproductions because they are, at best, only partial fragments of the entire original note’s total edge boundary. (See illustration 9 of the alleged “original printing plates” for the Green Box.)
Notes
 1. The following text is from the 1934 Subscription Bulletin: 300 exemplaries numérotés et signés d’un recueil de feuillets manuscrits,dessins et peintures (années 1911 à 1915) ayant servi à la composition du LA MARIÉE MISE A NU PAR SES CÉLIBATAIRES, MÊME par Marcel Duchamp Les notes manuscrites, en fac-simile rehaussé de crayon rouge et bleu, les dessins et peintures reproduits en phototypie (une planche en couleurs)sont imprimés sur papiers divers et réunis dans un emboîtage de 33 cm x 28cm. prix de l’exemplaire franco de port: France 120 francs / Étranger 150 francs Edition Rrose Sélavy 18 rue de la Paix Paris Il a été tiré 20 exemplaires (dont 10 hors commerce), signés et numérotés, sur papiers de luxe; chacune des boîtes contient, outre la reproduction en couleurs, des photographies originales et une page de manuscrit. prix de l’exemplaire franco de port: 750 francs. – Bulletin de Souscription Veuillez m’adresser ………………….. exemplaires de la boîte contenant les fac-simile et reproductions en couleurs de notes manuscrites, dessins, peintures ayant servi à la composition de LA MARIÉE MISE A NU PAR SES CÉLIBATAIRES, MÊME par Marcel Duchamp
1. The following text is from the 1934 Subscription Bulletin: 300 exemplaries numérotés et signés d’un recueil de feuillets manuscrits,dessins et peintures (années 1911 à 1915) ayant servi à la composition du LA MARIÉE MISE A NU PAR SES CÉLIBATAIRES, MÊME par Marcel Duchamp Les notes manuscrites, en fac-simile rehaussé de crayon rouge et bleu, les dessins et peintures reproduits en phototypie (une planche en couleurs)sont imprimés sur papiers divers et réunis dans un emboîtage de 33 cm x 28cm. prix de l’exemplaire franco de port: France 120 francs / Étranger 150 francs Edition Rrose Sélavy 18 rue de la Paix Paris Il a été tiré 20 exemplaires (dont 10 hors commerce), signés et numérotés, sur papiers de luxe; chacune des boîtes contient, outre la reproduction en couleurs, des photographies originales et une page de manuscrit. prix de l’exemplaire franco de port: 750 francs. – Bulletin de Souscription Veuillez m’adresser ………………….. exemplaires de la boîte contenant les fac-simile et reproductions en couleurs de notes manuscrites, dessins, peintures ayant servi à la composition de LA MARIÉE MISE A NU PAR SES CÉLIBATAIRES, MÊME par Marcel Duchamp
 2.Calvin Tomkins, Duchamp (New York: Henry Holt, 1996), 296.
2.Calvin Tomkins, Duchamp (New York: Henry Holt, 1996), 296.
 3.In Marcel Duchamp’s 1st Catalogue Raisonné designed by Duchamp himself in 1959 — Henri Pierre Roché, Duchamp’s close friend and sometime partner and collaborator writes about the Green Box notes: “These are exact replicas of each document with the original colors of the inks and pencils that he used. The textures and shapes of paper are identical with the originals even in the case of scraps and torn pieces where metal masks were used.” Robert Lebel, Marcel Duchamp (New York: Grove Press, 1959). 81.
3.In Marcel Duchamp’s 1st Catalogue Raisonné designed by Duchamp himself in 1959 — Henri Pierre Roché, Duchamp’s close friend and sometime partner and collaborator writes about the Green Box notes: “These are exact replicas of each document with the original colors of the inks and pencils that he used. The textures and shapes of paper are identical with the originals even in the case of scraps and torn pieces where metal masks were used.” Robert Lebel, Marcel Duchamp (New York: Grove Press, 1959). 81.
 4. Calvin Tomkins, Duchamp, 296.
4. Calvin Tomkins, Duchamp, 296.
 6.Elizabeth Cowling in the exhibition catalogue Surrealism and After:The Gabrielle Keiller Collection (Edinburg, 1997), 161.
6.Elizabeth Cowling in the exhibition catalogue Surrealism and After:The Gabrielle Keiller Collection (Edinburg, 1997), 161.
 7. David Joselit, Infinite Regress: Marcel Duchamp 1910-1941 (Cambridge:MIT Press, 1998), 85.
7. David Joselit, Infinite Regress: Marcel Duchamp 1910-1941 (Cambridge:MIT Press, 1998), 85.
 8. This particular note is recognized by experts as an authentic Green Box note original.
8. This particular note is recognized by experts as an authentic Green Box note original.
 9.This particular note is recognized by experts as an authentic Green Box note original.
9.This particular note is recognized by experts as an authentic Green Box note original.
 10.Ellis, Mosier, and McGilnchey identified the papers as wove and machine-laid.
10.Ellis, Mosier, and McGilnchey identified the papers as wove and machine-laid.
 11.For an English translation of the Green Box Notes, see Hamilton and Hamilton, The Bride Stripped Bare by her Bachelor, Even (New York: Percy Lund, Humphries and Co. Ltd,1960).
11.For an English translation of the Green Box Notes, see Hamilton and Hamilton, The Bride Stripped Bare by her Bachelor, Even (New York: Percy Lund, Humphries and Co. Ltd,1960).
 12.This particular note is recognized by experts as an authentic Green Box note original.
12.This particular note is recognized by experts as an authentic Green Box note original.
 13.See Hamilton for Green Box Notes.
13.See Hamilton for Green Box Notes.
 14.Duchamp was known for his formal interest in chance systems. For example,Duchamp and his two sisters created a musical score (also included in the Green Box) with a system of randomly selected notes.
14.Duchamp was known for his formal interest in chance systems. For example,Duchamp and his two sisters created a musical score (also included in the Green Box) with a system of randomly selected notes.













